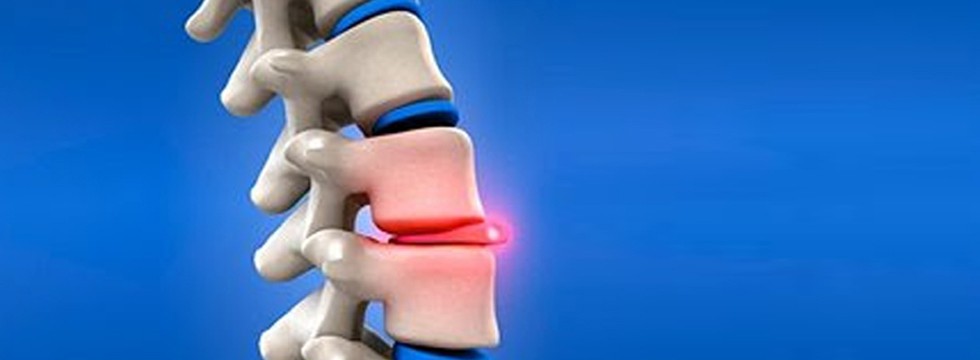
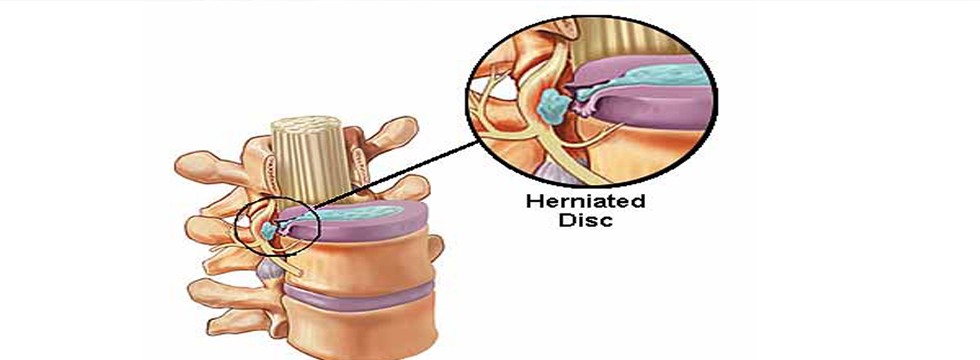
Prolapse Disc Treatment
Inter Vertebral Prolapse Disc bears 20-33 % of entire weight of vertebral column has two parts :-
- Nucleus pulposus – It is a mucoprotein gel containing various mucopolysaccharids has water content 70-90%. Its function is to resist and redistribute compressive forces within the spine.
- Annulus fibrosis – It is a fibro cartilage with bundles of collagen fibers (lamina) in a crisscross pattern. Its function is to withstand high bending and torsional load.
Prolapse Disc Clinical Features
- Herniated nuclear pulposus :- History of specific trauma.
- Leg pain in greater than back pain.
- Neurological deficit positive.
- Nerve tension sign positive.
- Pain increases with sitting and leaning forward coughing, sneezing, pain positive.
- Pain reproduced with ipsilateral SLR and Sciatic stretch test.
- Well leg SLR also produces pain.
- Annular Tear :- History of significant trauma.
- Back pain > leg pain.
- Leg pain bilateral and unilateral.
- Nerve tension sign positive.
Risk Factors
- Job requires heavy and repetitive weight lifting.
- Use of machine tools.
- Operation of motor vehicles.
- Cigarette smokers and tobacco consumers.
- Anxiety and depression.
- Stressful occupation as in doctors, police etc.
- Women with greater number of pregnancies.
- Obesity and other cardio-vascular risk factors.
- Monotonous work, working overtime etc.
- Improper postural habits.
Definitive Causes
- Degenerative changes makes disc susceptible to trauma. Any trauma with suddenly increases the pressure will result in rupture of posterior fibres of annulus e.g weight lifting, fall on buttock, direct trauma to back, twisting movements and occupational factors.
- During pregnancy labour and after prolonged bed rest due to disc softening.
- Disc rupture without any cause is due to degenerative process.
Physiotherapy Measures
- Rest 2 -3 days.
- Modalities – Thermotherapy.
- Heating- Hot pack, infra red, short wave, Ultra Sound, Tens.
- Cryotherapy – Ice pack and ice massage during first 24-48 hours is found to be very effective.
- Mobilization, manipulation, stretching, massage, traction,
- Corsets and braces to decrease pain and to recover the mobility of spine faster.
- Accessory mobility exercises, regional and segmental.
- Choices of exercises – a correct choice whether flexion or extension exercises has to be made depending upon the specific indications.