Tennis Elbow Physiotherapy Treatment
Tennis Elbow is defined as pain and tenderness in the lateral side of the elbow.
MOST COMMON
Tennis players (SERVE, BACKHAND STROKE)
May be occupational.
Other activities include: tightening a screw. Using a wrench, wringing washed cloths, vigorous hand shake
Painful elbow syndrome divided in following varieties :-
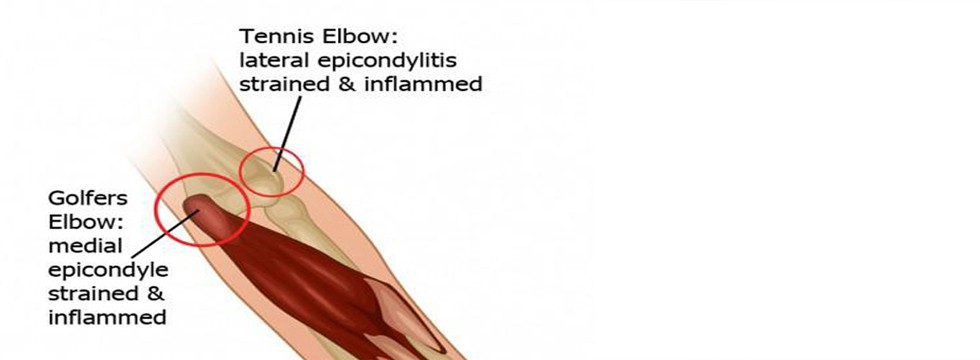
- Classical tennis elbow: lateral tennis elbow
- Other varieties
- Medial painful elbow(Golfer’s elbow)
- Posterior painful elbow around the margins of the olecranon process.
Causes of Tennis Elbow
Epicondylitis: due to single or multiple tears in common extensor origin, periosteitis, angiofibroblastic proliferation of extensor carpi radialis brevis.
Inflammation of adventitious bursa: between common extensor origin and radio humeral joint
Calcified deposits: within the common extensor tendon
Painful annular ligament: Due to hypertrophy of synovial fringe between radial head and the capitulum.
Pain of neurological origin: e.g. cervical spine affection, radial nerve entrapment, etc.
Symptoms of Tennis Elbow
Stage 1: acute inflammation but no angioplasty invasion patient complains of pain during activity.
Stage 2: chronic inflammation followed by some angioplasty invasion patient complains of pain both during rest and activity.
Stage 3: chronic inflammation with extensive angioplasty invasion patient complains of pain at rest, night and pain during activity.
Tennis Elbow Physiotherapy Measures
During Acute Phase
- Rest: above elbow pop splint with elbow in 90 0 flexion and supination with wrist in slight dorsiflexion
- Thermotherapy: heat modality like TENS, ultrasound, SWD in reducing pain.
- Cryotherapy: ice cold packs on tender area for 15-20 min is very effective.
- Electrical stimulation: done for 15-20 min with arm elevated to reduce pain and inflammation
- Massaging: gentle massing for next 10 days followed by frictional massage for the next 15 days
- Exercises: active exercises for shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. Isometric exercise helpful followed by pre in later stages
Post Acute Phase
- Patient instructed to avoid repeated wrist extension and supination movements.
- Strengthening exercises for extensor carpi radialis after a period of rest and support in acute phase.